-
About
- About Listly
- Community & Support
- Howto
- Chrome Extension
- Bookmarklet
- WordPress Plugin
- Listly Premium
- Privacy
- Terms
- DMCA Copyright
- © 2010-2025 Boomy Labs

 Steph Moy
Steph Moy
Listly by Steph Moy
In today's interconnected and data-driven world, IT disaster recovery has become a critical component of business continuity planning. Disasters can strike at any time, from natural catastrophes like earthquakes and hurricanes to cyberattacks and hardware failures. When such events disrupt IT systems and data, they can have devastating consequences for businesses. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to be well-prepared for these eventualities.
Source: https://www.secureworld.io/industry-news/it-disaster-recovery-best-practices
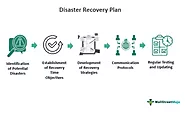
The foundation of IT disaster recovery readiness is a well-documented plan. This plan should detail the critical IT systems, data, and applications that need to be recovered in the event of a disaster. It should include procedures for data backup, recovery, and communication with employees and stakeholders. Furthermore, the plan should be regularly updated to reflect changes in the IT environment and business operations.
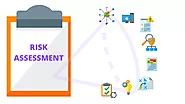
Understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to your organization is crucial. Conducting regular risk assessments helps identify and prioritize potential disaster scenarios. These assessments should encompass physical threats, cybersecurity risks, and potential operational disruptions. The results of these assessments can guide disaster recovery planning and resource allocation.

Data is often the lifeblood of any organization, and ensuring its safety and recoverability is paramount. Implement automated backup solutions that store data in multiple locations, both on-site and off-site. Cloud-based backups are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability and accessibility. Regularly test data recovery processes to ensure they work as intended.
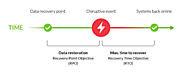
RTO and RPO are key metrics in disaster recovery planning. RTO specifies the maximum allowable downtime for specific systems, while RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss. These objectives should be clearly defined for each critical system, application, or data set to inform the recovery process and resources required.
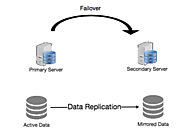
Redundancy in IT systems provides an additional layer of protection. Implementing failover systems ensures that if a primary system fails, a secondary system can take over seamlessly. This redundancy can be physical (e.g., duplicate servers) or virtual (e.g., load balancing for web applications). The goal is to minimize downtime and data loss.
