-
About
- About Listly
- Community & Support
- Howto
- Chrome Extension
- Bookmarklet
- WordPress Plugin
- Listly Premium
- Privacy
- Terms
- DMCA Copyright
- © 2010-2025 Boomy Labs


Listly by noluyolomtembu
An easily accessible alternative source of naturally generated colors is bacterial and fungal pigments. Nature produces many bio-dyes from various sources such as plants and microorganisms, and they have the potential to replace the synthetic dyes and pigments currently in use. Recent awareness of human safety and environmental protection has sparked renewed enthusiasm for natural color sources. Natural dyes or dyes of animal and plant origin are considered safe because they are inherently non-toxic, non-carcinogenic and biodegradable. The demand for natural colorants is increasing day by day as the current trend is a global shift towards the use of environmentally friendly and biodegradable raw materials. Bacterial pigments have a variety of benefits over other natural pigments, including rapid growth, straightforward processing, and weather resistance. Biological properties of microbial and bacterial pigments include antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer actions in addition to color.

The most characteristic feature of carotenoids is a series of long conjugated double bonds that form the central portion of the molecule. This gives shape, chemical reactivity and light absorption properties. . Carotenoids give the characteristic color to many foods .Carotenoids can be produced from fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals.
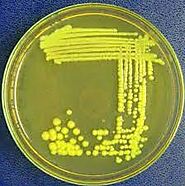
Yellow is definitely one of the most bright eye-catching colors. I am loving it!. The Yellow colonies can be clearly observed on the agar plate .Streptomyces sp produces carotenoids(carotene) which is an orange-yellow pigment.

The term carotene is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances which are synthesized by plants but cannot be made by animals . Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and (in low concentrations) yellow light.

Microbial cells accumulate pigments under certain culture conditions, which have very important industrial applications. Microorganisms can serve as sources of carotenoids. More than 750 structurally different yellow, orange, and red colored molecules are found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Carotenoids protect cells against photooxidative damage and hence found important applications in environment, food and nutrition, disease control, and as potent antimicrobial agents.

Carotenoids are essential pigments in photosynthetic organs along with chlorophylls. Carotenoids also act as photo-protectors, antioxidants, color attractants, and precursors of plant hormones in non-photosynthetic organs of plants.

Carotenoids are classified into two main groups: xanthophylls(yellow color, oxygenated) and carotenes(orange color ,non -oxygenated). Both types of carotenoids have antioxidant properties. In addition, some carotenoids can be converted into vitamin A, an essential component for human health and growth. You are protected from too much sunshine by xanthophyll carotenoids. They are most frequently connected to eye health. Plant growth is significantly aided by carotene carotenoids.