-
About
- About Listly
- Community & Support
- Howto
- Chrome Extension
- Bookmarklet
- WordPress Plugin
- Listly Premium
- Privacy
- Terms
- DMCA Copyright
- © 2010-2025 Boomy Labs

Listly by sanzbaij
This informative list points out the criticality of plagiarism, the most common types of plagiarism, as well as the measures that one can take to identify and avoid it. We’ll also look at how the expectations for academic writing might change in the future owing to digital advancements as the world becomes more digitally inclined.

Plagiarism.Org is an excellent website that teaches readers/viewers about plagiarism and the consequences of it, through videos and interesting articles.
Can words and ideas really be stolen...
Plagiarism is an act of FRAUD.
According to the Merriam-Webster online dictionary, to "plagiarize" means:
-to steal and use ideas or words of another as your own
-to use another's work without crediting the source
-to commit literary theft
-to present "new" ideas that have been derived from an existing source
Plagiarism is not only exclusive to academic writing works but also counts as copying media such as videos, music and images from others.

Check out this fun and informative PowToon (By Susie Jolliffe) that outlines how we can go about recognizing and avoiding plagiarism.
Main Points:
1. Plagiarism involves copying from either print or digital sources without crediting the author.
2. Incorrectly paraphrasing without citing the original author is also plagiarism.
3. Incorrect or Incomplete citations is also deemed as plagiarism (Referencing styles are very important).
4. Understand fair use when using video content or music from others.
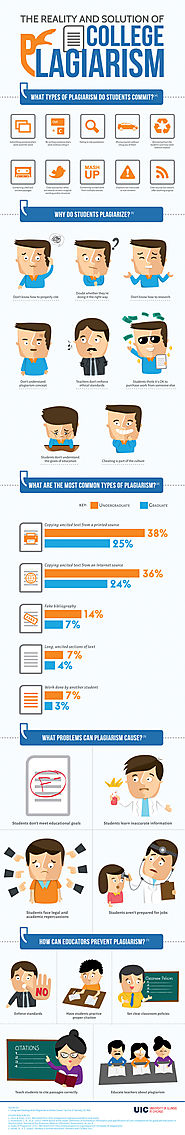
In this digital era with information readily at our fingertips, important delineations of content ownership are easily blurred. This infographic highlights the reality, consequences and solutions to avoid plagiarism.
Key Discussion Points:
1. Why do students plagiarise?
"Cheating is OK" mentality
Most common types of plagiarism is by undergraduate students
Problems that may arise from plagiarism
Inaccurate information may be learnt or shared
How can educators prevent plagiarism?

Direct Plagiarism
Direct plagiarism occurs when content from someone elses work is used word-for-word without citing the author, and without any quotation marks.
Self Plagiarism
Self-plagiarism occurs when a student re-submits parts of their own previous work in other modules/subjects/publications, without directly obtaining permission from the relevant lecturers involved.
Mosaic Plagiarism
Mosaic Plagiarism occurs when phrases are copied or "borrowed" from a source without using any quotation marks. This also occurs when substituting synonyms whilst keeping to the same general word and sentence structure of the original authors content.
Accidental Plagiarism
Accidental plagiarism occurs when an individual unintentionally omits citing or misquotes their sources. Incorrect paraphrasing using similar words without attribution also counts.
(https://www.bowdoin.edu/studentaffairs/academic-honesty/common-types.shtml)
Don't be termed a Plagiarist - The consequences surrounding plagiarism can be personal, professional, ethical, and legal. Plagiarism detection software such as Turnitin, allows guilty individuals to be caught easily and quickly.
(http://www.ithenticate.com/resources/6-consequences-of-plagiarism)

Professor Jonathan Zittrain closes the 5th International Plagiarism Conference, with a thought provoking keynote session on how to write in an internet environment.